Protocol Considerations For Emg
-
Real-world walking. Investigating gait during real-world activity is desirable to understand motor strategies in a natural environment although current technological limitations make long term recordings challenging.
-
Sample size. Greater numbers of participants and more stride cycles are necessary.
-
Muscle selection. Muscles representing all major muscle groups acting on the ankle, knee and hip joints in the sagittal and coronal planes should ideally be recorded to permit analyses of multi-muscle activation patterns and underlying neural control systems to be undertaken.
-
Electrode placement. A clear statement must be included regarding methods used to identify electrode placement and established guidelines followed.
-
Longitudinal studies. This will inform us how motor patterns change with age and disease progression and help establish EMG characteristics as biomarkers.
-
Additional gait and cortical parameters. Parameters such as joint kinematics and kinetics as well as cortical activity measured with mobile, wireless systems such as functional near infrared spectroscopy or electroencephalography will enable us to relate EMG to gait impairment and cortical processes.
Clinical And Demographic Features
Table compares the demographic characteristics of the 38 patients with PD and 16 patients with other forms of parkinsonism that completed our work-up. Patients with PD were older than patients with parkinsonism . However, age of onset, disease duration and gender distribution were similar in both groups, despite a trend for higher percentage of women in the parkinsonism group and for older age of onset and longer disease course in the PD group. Mean Hoehn and Yahr scores in the PD group were 2.6±0.1 . Most of the PD patients were treated with levodopa and 68.8 % of the parkinsonism group were taking levodopa. A third of the PD patients and 31 % of the parkinsonism group were treated with pramipexol while 38.9 % of the PD and none from the parkinsonism group were treated with amantadine and only 8.3 and 18.8 were treated with biperiden.
Table 1 Demographic characteristics and risk factors for neuropathy in patients with Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonism
Peripheral Neuropathy In Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease
| Cognitive dysfunction |
| Arrhythmias and other cardiovascular manifestationsOrthostatic hypotensionUrinary urgency, incontinence or nocturiaGastrointestinal manifestations including constipationThermoregulatory dysfunction including change in sweating function |
| Sleep disorders |
| Periodic limb movements/restless legs syndromeExcessive daytime somnolence |
| Visual disturbances including lack of accommodationSeborrhoeic dermatitis |
Read Also: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Read Also: Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease Success Rate
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
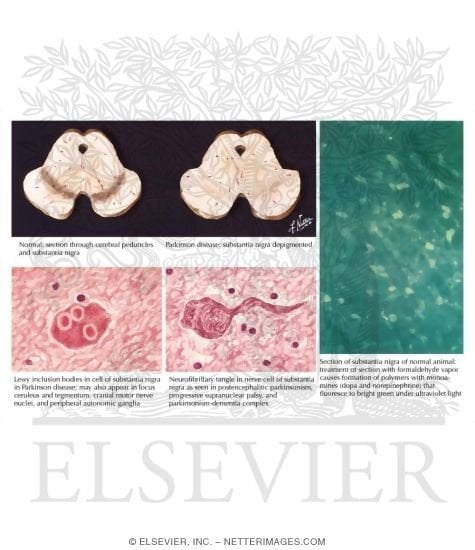
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Parkinsons Without Shaking
Don’t Miss: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Treatment Options For Peripheral Neuropathy In Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease Patients
In our initial case series with IPD patients identified to have peripheral neuropathy , all patients identified to have one of cobalamin deficiency, methylmalonic acid elevation, or elevated homocystine levels were prescribed monthly intramuscular injections of 1000 µg of cobalamin . This was provided via intramuscular injections and not oral therapy due to concerns of potential inadequate absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. All patients initialized on therapy were subjected to repeated clinical examinations using the Toronto Clinical Scoring System and electrophysiological evaluations at 6, 12, and 24 months after diagnosis of the peripheral neuropathy when cobalamin therapy was initiated. Repeated blood tests for cobalamin, fasting methylmalonic acid and fasting homocysteine were concurrently performed.
Stooping Or Hunched Posture
People who have Parkinsons disease may notice changes in their posture due to other symptoms of the disease, such as muscle rigidity.
People naturally stand so that their weight is evenly distributed over their feet. However, people who have Parkinsons disease may start bending forward, making them appear hunched or stooped over.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons And Marriage Breakdown
You May Like: Weighted Silverware
Neuropathy In Parkinsons Disease Patients With Intestinal Levodopa Infusion Versus Oral Drugs
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Charité – University Medicine, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Charité – University Medicine, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Charité – University Medicine, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Charité – University Medicine, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, St. Joseph-Hospital, Berlin-Weissensee, Germany
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Charité – University Medicine, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany
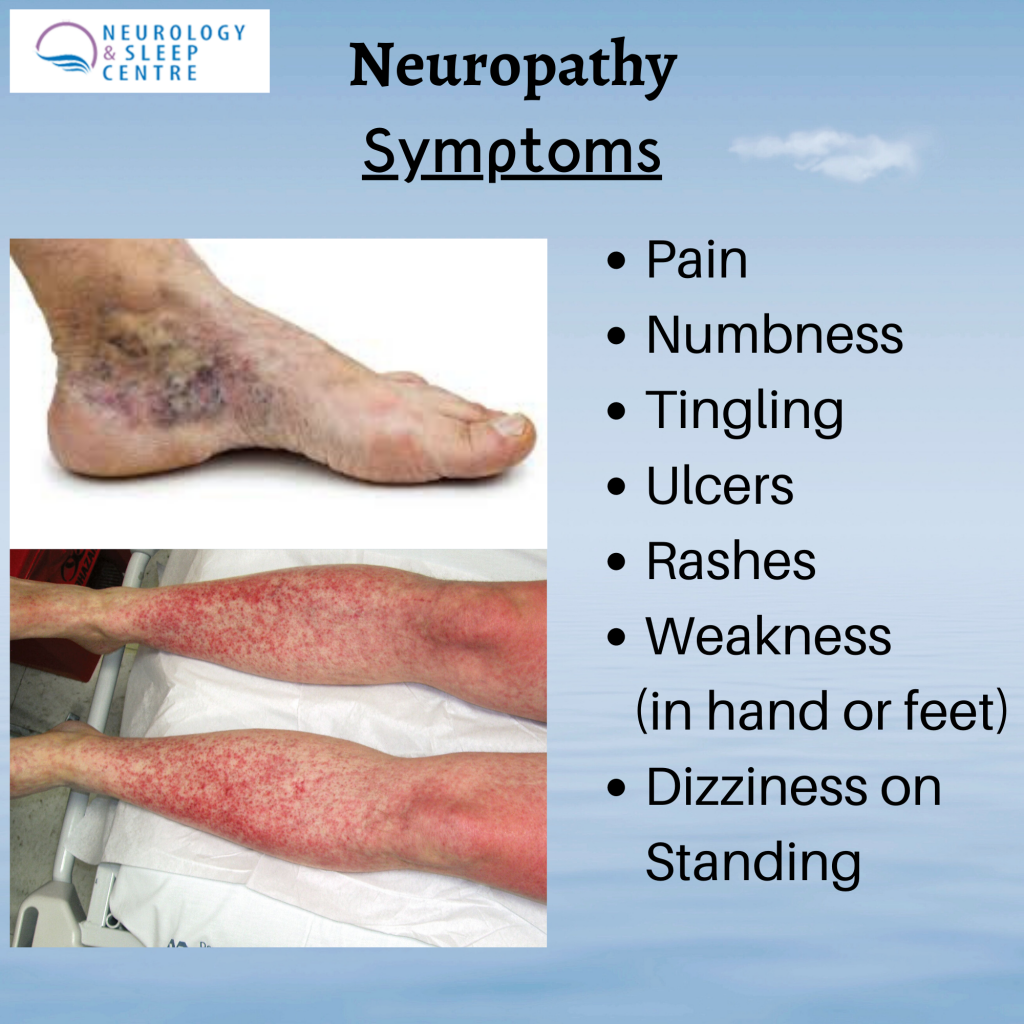
Symptoms Of Peripheral Neuropathy
The symptoms of PN can be non-specific, and a person therefore may not be able to distinguish on their own whether his/her symptoms are due to PN or another condition. PN, however, often results in specific findings on a neurologic exam, such as decreased sensation to pin prick or vibration or the lack of ability to discern which way a toe is being pointed without looking. Other tests such as Electromyogram and Nerve conduction studies may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Small fiber neuropathy which typically causes pain, burning, tingling and/or numbness in the feet, may have normal EMG and NCS and a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. With the appropriate examination and supportive tests however, a neurologist should be able to distinguish the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy from other conditions, including PD, that may cause similar symptoms.
There are many known causes of PN including diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, certain infections, and autoimmune diseases. Many of these causes can be treated, so it is important to know if you do have PN and what the cause is. There are those people however, who have the signs and symptoms of PN, but no known cause can be identified.
Read Also: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinsons. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Also Check: Gift Ideas For Parkinson Patients
Results Of Large Fiber Neuropathy Assessment
NCS/EMG was performed in 39 patients . 12 out of the 26 PD and 4 out of the 13 from the parkinsonism group had abnormal NCS/EMG results. As expected, patients with abnormalities suggestive of peripheral neuropathy on the screening neurological exam were more likely to have abnormal EMG . Neuropathy prevalence was similar in the groups with PD and parkinsonism , whether PN was assessed by SWT, NCS/EMG or clinically .
Fig. 1
Part a shows mean peroneal compound motor action potential amplitudes and mean sural sensory nerve action potential amplitudes in patients with Parkinsons disease . PD all patients refers to mean values from the whole group , PD no PN refers to mean values from PD patients without large fiber neuropathy, PD SFN refers to patients with PD and small fiber neuropathy and PD Neuropathy to mean values in patients with PD and large-fiber neuropathy. Part b shows mean values of peroneal motor and sural sensory conduction velocities in the same groups
Fig. 2
Recommended Reading: On Off Phenomenon
How Does Alcohol Affect Parkinsons Symptoms
In general, alcohol can be harmful to people with chronic conditions. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , overconsuming alcohol can be a long-term risk factor for a weakened immune system, learning and memory problems, high blood pressure, digestive issues, and various types of cancer. When looking specifically at Parkinsons symptoms, however, reports differ on how alcohol and PD may be linked.
The type of alcoholic beverage consumed may affect whether drinking has an impact on PD. A 2013 study found that the risk for developing Parkinson’s disease appeared to increase depending on the amount of liquor consumed, although no link was conclusively found between drinking wine and the development of PD.
In terms of how long-term alcohol use affects the risk of PD, one study published in 2013 followed people who had been admitted to the hospital with alcohol use disorders for up to 37 years. The study authors found that a history of alcohol abuse increased the risk of admission into the hospital for Parkinsons for both men and women. The study authors suggested that chronically drinking too much alcohol can have neurotoxic effects on dopamine, the neurotransmitter in the brain that is relevant to Parkinson’s disease.
There may also be factors other than observable symptoms such as how alcohol interacts with your medication that are important to consider when making decisions about your lifestyle and drinking habits.
Corneal And Intraepidermal Nerve Fibers
Twenty-six PD patients and 26 controls underwent CCM and 24 PD patients and 10 controls underwent skin biopsies. Both CNFD and IENFD were significantly lower in PD patients compared to controls . However, CNBD was significantly higher in PD patients compared to controls , P < 0.001). CNFL was also significantly higher in PD patients .
Mean ± SEM of corneal nerve fiber density , intraepidermal nerve fiber density , corneal nerve fiber branch density and fiber length in Parkinson’s disease compared to controls with significance level and effect size.
Both IENFD and CCM parameters displayed asymmetry between sides in PD patients. However, when CCM measures and IENFD were separated according to the clinically more affected side and the clinically less affected side there was no significant difference in CCM measures or IENFD.
Also Check: Zhichan Capsule
Clinical Neurophysiological Quantitative Sensory And Autonomic Measures Of Neuropathy
NDS, DB-HRV and sensory thresholds all showed impairment in PD compared to controls . Overall, there was no significant postural drop in blood pressure in PD . Three out of 27 PD patients had large fiber axonal neuropathy on nerve conduction studies and 2 of these patients had raised methylmalonate. However, methylmalonate was raised in a further 4 PD patients with normal nerve conduction studies. Homocysteine was raised in 5 patients all of whom had normal neurophysiology. All patients had normal vitamin B12 and folate levels. Protein electrophoresis was normal in patients with large fiber neuropathy.
Clinical And Demographic Profiles
A total of 75 PD patients were evaluated of whom 65 were included in the study. Among the 10 patients excluded, 7 had impaired glucose tolerance and 3 had corneal disease. The demographic and clinical profiles of PD patients and controls are summarized in Table . There were no significant differences in age, gender, education levels, BMI, plasma cholesterol, VitB12, and homocysteine concentrations between control and PD patients. As shown in Table , the MoCA scores were lower in PD patients than in the control group .
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of participants.
The AUC distinguishing PDD from PD-CN for CNFD, CNBD, and CNFL was 96.67% , 90.12% , 84.44% , respectively. Using a CNFD cutoff of < 25.00 no./mm2, the sensitivity and specificity for PDD was 86.67% and 96.30%. Using a CNBD cutoff of < 20.47 no./mm2, the sensitivity and specificity for PDD was 73.33% and 96.30%. Using a CNFL cutoff of < 12.29mm/mm2, the sensitivity and specificity for PDD was 66.67 and 100%. Furthermore, a combination of three parameters resulted in an increased AUC of 98.27% , the sensitivity and specificity was 100% and 88.89%, respectively .
Don’t Miss: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
Autonomic Dysfunction And Parkinson’s
Autonomic dysfunction often occurs in Parkinsons due to the loss of dopamine-producing cells and the presence of microscopic protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain. As a result, a number of non-motor symptoms may be experienced. Research suggests that the peripheral nervous system may be affected long before such symptoms appear.
If autonomic dysfunction is severe, atypical parkinsonism, such as multiple system atrophy , should be suspected.
Please click on the links below for information on individual symptoms related to ANS dysfunction:
- bladder problems including urgency, frequency, incontinence and night time urination
- constipation and weight loss
- swallowing difficulties .
Scientists now recognise that many medications used to treat Parkinsons can affect the ANS and so make symptoms worse. It is important to monitor your medications and symptoms so that you can discuss these with your doctor. He or she may then be able to adjust medications to reduce the impact on the ANS and so improve symptom control. See Keeping a diary for more information on this and how it can help.
Research suggests that about 90% of people with Parkinsons experience autonomic dysfunction which may considerably reduce quality of life.
Peripheral Neuropathy And Parkinsons Disease
A number of studies have tried to determine if PN is more common among people with PD as opposed to people without PD. PN is a relatively common condition in the general population, which makes it difficult to ascertain whether or not it is even more common among people with PD.
The available studies have varying results and are difficult to compare with each other as they:
- Include different types of populations of people with PD
- Assess peripheral neuropathy differently
- Assess for causes of peripheral neuropathy differently
A recent review looked at all the available data and determined that large fiber neuropathy was present in 16% of patients with PD, about double the prevalence of this condition in the general population. Skin biopsy-proven small fiber neuropathy was present in over 50% of people with PD, although this result was based on a small sample of patients.
Read Also: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Relation Between Corneal Nerve Parameters Intraepidermal Nerve Fibers And Clinical Features
CNFD correlated positively with IENFD in PD patients . Correlations between CCM parameters, IENFD and clinical data are summarized in Table 2. CNBD and CNFL but not CNFD correlated inversely with UPDRS-III. There was no correlation between any of the corneal nerves parameters and disease duration, cumulative Levodopa dose, non-motor symptoms, pain scales or sensory thresholds. However, there was an inverse correlation between heat-induced pain threshold and SFMPQ . A significant positive correlation was found between DB-HRV and all corneal nerve parameters, but not IENFD . However, IENFD correlated with disease duration, disease severity and cumulative Levodopa dose. Both CNFD and IENFD correlated with NDS. CNFD, IENFD and NDS were independent of vitamin B12, folate, methylmalonate and homocysteine levels.
Spinal Lesion Or Tumor
A spinal lesion or tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue within or surround the spinal cord or column. Spinal tumors can be cancerous or noncancerous, and originate in the spine or spinal column or spread there from another site.
Back pain, which is worse at night or increases with activity, is the most common symptom. If the tumor presses on a nerve, it can cause numbness or weakness in the arms, legs, or chest.
Treatment depends on the type and location of the lesion or tumor, and whether or not its cancerous or noncancerous. Surgery to remove the tumor, or radiation therapy or chemotherapy to shrink the tumor, can usually resolve leg weakness.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is also known as Lou Gehrigs disease. Its a progressive neurological disease that damages nerve cells and often begins with muscle twitching and weakness in the legs.
Other early symptoms include:
- slurred speech
- difficulty holding up your head
Theres currently no cure for ALS, but treatments are available that can help control symptoms and complications and improve quality of life.
Also Check: Similar To Parkinsons
Parkinsons Disease And Alcohol: Your Guide
If you have Parkinsons disease , you may be wondering whether alcohol consumption affects the development or progression of your condition. Some people may wonder if they should avoid drinking completely. As one MyParkinsonsTeam member asked, How does alcohol affect Parkinsons how much can I drink? Or should I avoid drinking altogether?
Some studies havent found that small amounts of alcohol are associated with a higher PD risk, while others highlight the dangers alcohol can pose for anyone with a chronic condition. In addition, there may be adverse interactions between alcohol and common Parkinsons medications. Because of conflicting information, people with PD may feel confused about whether or not to drink.
Ive been told by more than one doctor that I should not have any alcohol, one MyParkinsonsTeam member wrote. And at this point, I dont remember which doctor or specifically why.
So, how do you decide what approach to take?
If you have Parkinsons disease and are trying to decide whether or not to reduce your drinking or quit alcohol completely here are some things to consider.